Credit Value Adjustment (CVA) is aimed to express the difference between the risk-free portfolio value and the true portfolio value that takes into account the probability of counterparty default. This paper, together with other documents published in this series by the author, presents guide into methodology of CVA computation for derivatives. We demonstrate main steps to price Counterparty Credit Risk and compute the unilateral CVA for a portfolio of interest rate swaps.
Category: How To
We present review of margining as Credit Counterparty Risk mitigation tool in OTC derivative trading based on International Swap and Derivative Association standards. Practical part of paper contain demonstration of impact of margining thresholds, amounts and timing parameters on portfolio exposure.

We just have published white paper about close-out netting in Credit Counterparty Risk.
The paper presents brief summary of netting principles and effects in Counterparty Credit Risk. We discuss advantages, types of netting and main concepts for institutions with derivative portfolios.

From the practical point of view, we first implement concept of netting with simple examples and then show netting effects for simulated portfolios of derivative transactions. In addition to collateral and margining, netting is one of main methods of CCR mitigation.
The full text of white paper is available at our Research Papers page. You can also download it by the link below:
Our latest white paper provides practical guidelines on estimation of Exposure at Default, CCR default capital charge and standardized CVA capital charge, based on the methods proposed in Basel 2 and 3, and compares the capital charge imposed under different methods (Current Exposure Method, Standardized Method, Internal Model Method, and the recently proposed Non-Internal Model Method) and risk weighting approaches (Standardized and Internal Risk Based), using the calculations performed for a portfolio of derivatives in PrevioRisk software.
The results of practical implementation show that Internal Model Method of EAD estimation produces about a quarter (27-28%) lower CCR capital charge than Standardized and NIMM methods. Particularly, IMM allows to recognize fully the effect of netting and margining, and saves capital for trades influenced by market factors with low volatility. In addition, the results confirmed that IRB risk weighting approach results in lower required capital estimates than the Standardized one, with capital relief from IRB implementation reaching 35-40%.
The full text of white paper is available at our Research Papers page. You can also download it by the link below:
When a bank does not have regulatory approval to use Advanced CVA capital charge, which allows to calculate regulatory capital on counterparty-by-counterparty basis, the bank must calculate capital on portfolio level using the following formula (see Basel III: A global regulatory framework for more resilient banks and banking systems para. 103).
As was mentioned above, this is formula for Standardized CVA capital charge calculated at portfolio level, which in the given form does not allow to define main drivers and components of CVA capital charge. For this purpose we use
decomposition, based on EAD on customer or even trade level. As we will see, it is possible to manage portfolio
by hedging separate trades. Here is the example of CVA capital decomposition for portfolio of 250 derivatives with total notional of 4.5 bln (all numbers are in USD mln).

Delta sensitivities are usually computed to show Present Value response to 100% change in underlying market factors.
However, we can define risk factor, which has the highest expected impact on Present Value.

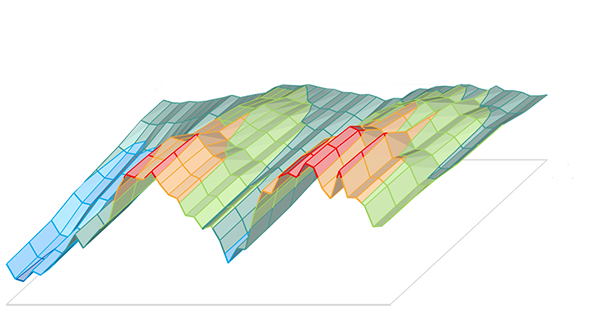
One of the typical tasks when constructing stress-test scenario is risk factor selection. Obviously, each portfolio has trade-specific factors which directly influence present value (PV) and potential future exposure (PFE) of positions and, thus, overall risk exposure and performance of the portfolio. For example, credit default spreads are needed to price Credit Default Swaps.
In most cases, however, there are global macroeconomic factors (GDP, interest rates, oil price etc.) and market-specific time series (such as market indices and key market drivers), which have indirect influence on trade-specific factors and, thus, portfolio value. This relationship can be measured ether by correlation, if relationship has no lag, or by autocorrelation, in case of lagged effect.
The delta equivalents of a position describe the response of a position/portfolio to a change in the market data.
Delta equivalent is the derivative of the Present Value with respect to a given risk factor, multiplied by the value (price) of that particular risk factor:
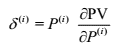
Read more…
Marginal Expected Exposure (Marginal EE) represents the effect of each specific contract on aggregated Expected Exposure of the portfolio. This concept is useful for understanding which trades are contributing most to the total portfolio risk, as well as for assessing the return on a specific trade against its contribution to total exposure. If portfolio includes only one contract, then Marginal Exposure of this contract equals to portfolio exposure.
The goal is to find allocations of that reflect
trade contribution to the overall risk for each period
and sum up to the counterparty-level
.